Previous Projects
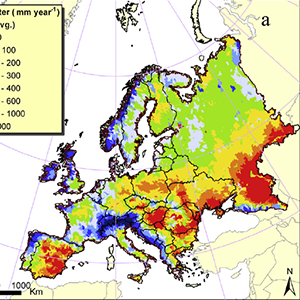
A Continental-scale Hydrology and Water Quality Model for Europe
A combination of driving forces is increasing pressure on local, national, and regional water supplies needed for irrigation, energy production, industrial uses, domestic purposes, and the environment. In many parts of Europe groundwater quantity, and in particular quality, have come under sever degradation and water levels have decreased resulting in negative environmental impacts.
Water resources of the Black Sea Basin at high spatial and temporal resolution
The pressure on water resources, deteriorating water quality, and uncertainties associated with the climate change create an environment of conflict in large and complex river system. The Black Sea Basin (BSB), in particular, suffers from ecological unsustainability and inadequate resource management leading to severe environmental, social, and economical problems.
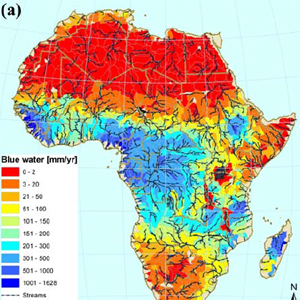
Continent of Africa Water Resources Availability
Accurate knowledge of freshwater availability is indispensable for water resources management at the regional or national level. In this project we estimated the freshwater availability of the continent of Africa at a subbasin level and monthly intervals using advanced modeling tools.
This project served as a precursor of a following one, where we modelled the impacr of climate change on water resources of African continent.
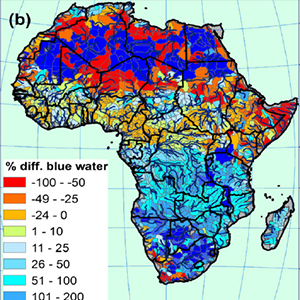
Impact of climate change on water resources
This project analyzes the impact of climate change on freshwater availability in Africa at the subbasin level for the period of 2020–2040. Droughts can have devastating effects on water supply, crop production, food security and many other aspects of human livelihood. The impact is particularly severe in Africa where subsistence farming dominates the food production and where political, social, and economic systems are often inadequately prepared to cope with disasters.
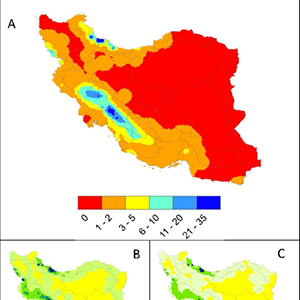
The future of extreme climate in Iran
Iran is experiencing unprecedented climate-related problems such as drying lakes and rivers, dust storms, record-breaking temperatures, droughts, and floods. Here, we use the ensemble of five high-resolution climate models to project maximum and minimum temperatures and rainfall distribution, calculate occurrences of extreme temperatures (temperatures above and below the historical 95th and 5th percentiles, respectively), analyze compound of precipitation and temperature extremes, and determine flooding frequencies across the country.
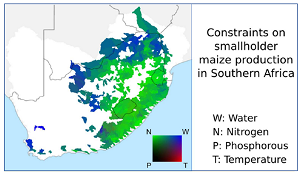
Improving crop yield and water productivity in Southern Africa
This project quantifies the potential effects of a set of technologies to address water and fertility constraints in rainfed smallholder agriculture in South Africa, namely in situ water harvesting (WH), external WH, and ecological sanitation (Ecosan, fertilization with human urine). We used the Soil and Water Assessment Tool to model spatiotemporally differentiated effects on maize yield, river flow, evaporation, and transpiration.
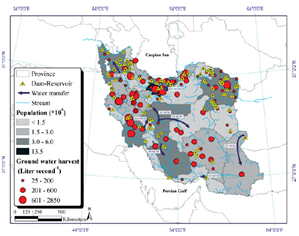
Renewable Water Resources of Iran
Knowledge of a country's internal renewable water resources is strategic information needed for the long-term planning of a nation's water and food security, among many other needs. New modeling tools allow this quantification with high spatial and temporal resolution. In this study, we used the program Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) in combination with the Sequential Uncertainty Fitting program (SUFI-2) to calibrate and validate a hydrologic model of Iran based on river discharges and wheat yield, taking into consideration dam operations and irrigation practices.
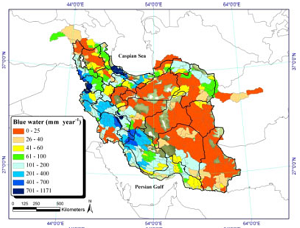
Impact of climate change on renewable water resources of Iran
As water resources become further stressed due to increasing levels of societal demand, understanding the effect of climate change on various water cycle components is of strategic importance in managing this essential resource. In this study, we used a hydrologic model of Iran to study the impact of future climate on the country's water resources.
Alleviating water scarcity through intra-country virtual water trade
In many parts of the world, food production is threatened by increasing occurrences of water scarcity. The suggestion of using virtual water trade (VWT) between countries has been put forward to alleviate water scarcity in international trades. In this project, we analyzed the potentials of VWT between provinces of Iran, which is achievable, in part, by structural changes in cropping pattern (SCCP).
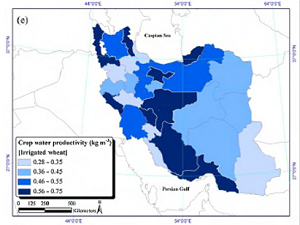
Assessment of Wheat Production in Iran
Water scarcity is a threatening problem to the sustainability of agricultural production in many world regions. Wheat is a strategic and dominant crop and the most extensive irrigation water user in Iran. Hence, understanding wheat's "crop yield–water" relations across the country is essential for sustainable production and policy directions for future investments. We estimated that 88% of the additional required wheat must be produced in already water-stressed provinces sounding the alarm for future food security in the region.

Technical Papers on Calibration of Hydrologic Models and the Associated Uncertainties
1) Hydrological modelling of the Chaohe Basin in China: Statistical model formulation and Bayesian inference
Calibration of hydrologic models is very difficult because of measurement errors in input and response, errors in model structure, and the large number of non-identifiable parameters of distributed models. The difficulties even increase in arid regions with high seasonal variation of precipitation, where the modelled residuals often exhibit high heteroscedasticity and autocorrelation.

Technical Papers on Calibration of Hydrologic Models and the Associated Uncertainties
2) Uncertainty analysis techniques: Application to the Chaohe Basin in China
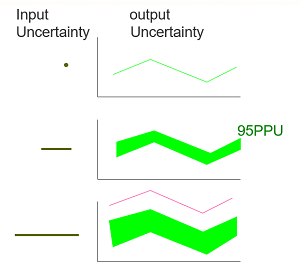
Distributed watershed models are increasingly being used to support decisions about alternative management strategies in the areas of land-use change, climate change, water allocation, and pollution control. For this reason, these models must pass through careful calibration and uncertainty analysis. In recent years, scientists have come up with various uncertainty analysis techniques for watershed models to fulfill this demand.
Technical Papers on Calibration of Hydrologic Models and the Associated Uncertainties
3) The Fallacy in the Use of the "best-fit" Solution in Hydrologic Modeling
To use ng the parameters associated with the best-fit simulation (i.e., the simulation with the highest objective function value) to represent a calibrated hydrological model. The reason is that the calibrated model's best objective function value is usually not significantly different from the next best value or the values after that. However, this non-uniqueness of the objective function values causes a problem because the best solution's parameters are often significantly different from the next best set of parameters.
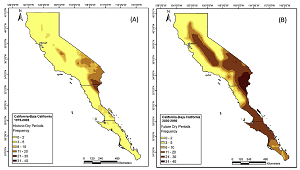
Extreme Climate Analysis in California
Application of our Climate Change Toolkit (CCT) in California using ensemble results of scenario RCP8.5 showed a probable increase in the frequency of dry periods in the southern part of the region while decreasing in the north. The frequency of wet periods may suggest higher risks of flooding in the north and coastal strips. We further found that every county in northern California may experience flooding conditions of 1986 at least once between 2020 and 2050.